Solutions>Conventional Power Solutions>Commercial UPS
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is an electrical device provides clean power to a load when the input power source -typically the mains utility - is unstable or fails. The UPS provide a complete protection from all input power disturbances without interruptions by means of one or more attached batteries and associated electronic circuitry. UPS is typically used to protect computers, data centers, telecommunication equipment, Medical equipment, and all sensitive electrical equipment from the input power disturbances e.g. Sags, Spikes, transients, lightning effects, Noise, Harmonics, frequency fluctuations....etc. which cause injuries, fatal damage, serious business disruption and/or data loss.
UPS Topologies:
UPS's are divided to three main classes as per EN62040-3. The Stand-by (Off Line) UPS is the simplest and the least expensive, then comes the Line Interactive type, which overcomes the major disadvantages inherent to the off-line unit, finally the Double Conversion (On-Line) UPS which provides the best power protection.- Passive Stand-by UPS
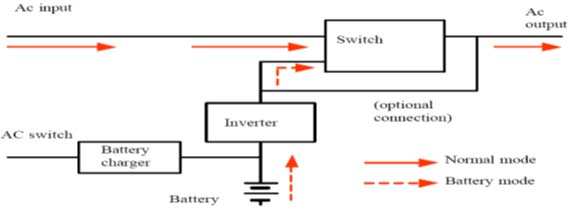
A Stand-by, also called off-line UPS or Backup, feeds the load continuously from Mains. Upon mains outage, the load connections transferred to the inverter fed from the batteries. Most of the short term spikes surges and high frequency harmonics are decayed by means of special filters. While various phenomena of transient nature during mains existence, like over voltages can harm protected data.
These units are generally equipped with spike suppressors, aimed to protect the hardware from high voltages on the utility grid.
Off-line systems are used mainly for low power installations, small offices, personal home computers and other less critical application, where eliminating 85% to 90% of computer malfunctions caused by power failure, is satisfactory.
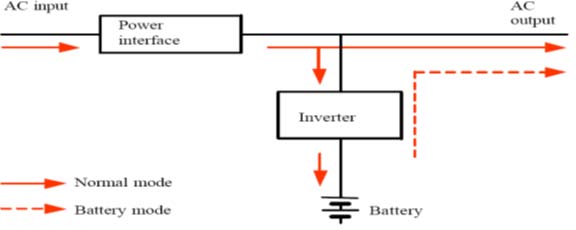
- Line Interactive UPS
Line Interactive UPS, called sometimes Interactive UPS, or On Line Interactive UPS. These systems are also based on stand-by principle,working directly from mains, switching to battery (via the inverter) upon mains disappearance with additional circuits filter and correct output voltage, keeping it within allowed tolerance band, thus providing conditioned power to the critical load.
Line Interactive UPS units come generally in the range of 500 to 5000 VA, offering a popular solution for personal computers, hubs and other loads in this power range. These units are used mainly for short backup times sufficient to shut down.
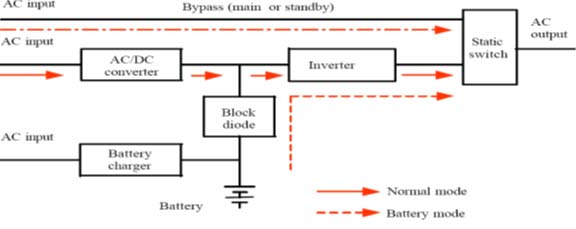
- Double Conversion UPS with Bypass
A Double Conversion, also called On-Line UPS, or True On-Line UPS, is the ultimate solution for all applications from 1 kVA up to 1 MVA sized consumers. Here, the load is constantly fed from the Inverter, providing conditioned, stabilized sinusoidal voltage. The utility line in these systems forms a backup source in case of UPS malfunction. The Transfer switch will automatically transfer the load to mains in case of overload or UPS failure.
The On-Line unit comprises two converting stages; the first stage converts the incoming AC power to DC, thus creating a DC-buss, which is fed either from mains or from storage battery, the second stage converts the DC power back to conditioned AC in order to feed the critical load. Filters on the DC buss and fast regulating circuits in the converters practically isolate the load from any abnormal utility behavior.
The following merits of Double Conversion systems make it the preferred choice for most business applications:-
It offers the best power protection, covering any and all types of mains disturbances.
There is no size limit.
With the right system, no practical limit exists on the available back-up time.
Units can be connected in parallel redundant configuration, for increasing reliability.
In addition, this is the best choice, considering such issues as modularity, ability to work from generator, power factor correction, maintenance, hot swapping, fault clearing, supervising, and communicating.
UPS Selection Guide:
- Decide the required size of the UPS (VA & Watts) to decide Power Capacity of the required UPS, you should decide which consumers should be protected and its power consumption in Amps, VA, or Watt.
- Decide the required Autonomy time (Back-up time) Autonomy time is the time that batteries are able to back-up operation and feed the load upon failure of utility power. Load consumption and size of UPS batteries dictate the back-up time.
- Decide the type of the UPS you need UPS's are roughly divided to three main classes. The Off Line (Stand-by) UPS is the simplest and the least expensive, then comes the Line Interactive type, which overcomes the major disadvantages inherent to the off-line unit, finally the Double Conversion On-Line UPS which provides the best power protection.
- Estimate the required Reliability you should consider Reliability issues if you provide real time service e.g. Reliability, Availability, MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures), MTTR – Mean Time To Repair, and Availability [A= MTBF/(MTBF + MTTR)] , are the basic functions for measuring UPS non-failure probability. The reliability of stand-alone on-line UPS is about 0.91 and for high mission requirements need more Reliability figures,an additional Redundant UPS can be connected to work in parallel with the first unit,and normally both units share the load. When one unit fail the second will continue to feed the load and the Reliability figure will increase to 0.993, adding additional redundant units increases the Reliability to any desired value.
- Refine the deal at these stage you should already know the KVA rating of the UPS you intend to buy, the type of the UPS (Standby/Line Interactive/On-Line), the autonomy time needed, and the configuration (Stand alone or Redundant).
Tips to help you while concluding your Power UPS deal:
- Increase UPS capacity to allow for future expansion.
- Don't buy back up time that you don't need. Longer backup time does not mean better UPS.
- In case of Online units make sure you can add external batteries in future and that you can increase power by adding parallel units if expected.
- Don't buy any extras if you are not sure that they are needed for your application, Most can be added in the future whenever required.
- Make sure that the UPS includes surge protectors on input and on its communication lines.
- Make sure that the UPS performs automatic battery tests, warning whenever the batteries should be replaced.
- Avoid confusion of misleading terms; Smart UPS should regulate output. Semi-sinusoidal output is not sinusoidal. On -Line must be double conversion and be able to regulate output frequency. Note that "Automatic self-test" does not always mean battery test as well.
- Backup time has no meaning if you don't consider the amount of UPS loading. Partial load increases the time the battery backs-up the equipment.
- When purchasing the UPS, make sure that after sales service is in good hands.
- Check Guarantee. Duration, Where and When?
- Make sure that manufacturing company is at least ten years in the UPS business.
